Graphene in 3D printing is the thinnest and strongest material and also an excellent electrical and heat conductor that has unique optical properties. Graphene is a 2D material made of carbon atoms, arranged in a honeycomb lattice. Its myriad qualities make graphene worthy of the title “wonder material”, with endless potential for all sorts of applications from membranes to electronics.
Graphene-enhanced nanocomposite materials greatly improve traditional materials used in 3D printing, like plastics. Graphene nanoplatelets can be added to polymers to create materials that are mechanically stronger and boast improved thermal and electrical conductivity.
Graphene significantly enhances the mechanical properties of 3D printed objects due to its unique structural characteristics and integration into various composite materials. This improvement is evident in applications such as fuel cells, bioprinting, and nanocomposites.
Utilizing Graphene in 3D Printing
Properties of Graphene exploited in 3D Printing
Incorporating Graphene in 3D printed composites imparts enhanced mechanical strength, elastic modulus and increase in ultimate strength. This enables creation of lightweight yet strong structures. Graphene-polymer composites show their suitability for demanding applications like fuel cells.
3D Printed composites which incorporate graphene oxide, makes the product versatile especially in SLA resins & enhances mechanical performance under stress, addressing the limitations of traditional SLA materials.
In bioprinting, graphene-based materials, improve the mechanical and biological properties of constructs, making them ideal for tissue engineering.
Customization and Conductivity Reduced graphene oxide in 3D printing allows for complex geometries with tailored mechanical and electrical properties, offering both strength and conductivity.
Applications of Graphene In 3D Printing
Graphene-based 3D printing is revolutionizing various industries due to its unique properties, including high electrical and thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance. The following sectors are particularly benefiting from these advancements:
Electronics: Graphene’s excellent conductivity makes it ideal for applications in electronics, such as sensors and electrochemical electrodes. The integration of graphene in 3D printed components enhances performance in devices like batteries and supercapacitors, leading to improved energy storage solutions.
3D Bioprinting with Graphene: One of the most exciting applications of 3D-printed graphene is in the field of bioprinting. This technique allows for the creation of implants and tissue scaffolds for organ restoration and regeneration. Graphene-based materials enhance the thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties of these scaffolds, making them suitable for both hard and soft tissue engineering. For instance, 3D-printed graphene scaffolds have shown promise in bone regeneration and neural tissue engineering, offering improved biocompatibility and mechanical strength.
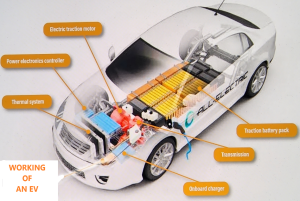
 Aerospace and Automotive: The lightweight and durable nature of graphene composites is advantageous in aerospace and automotive industries, where reducing weight while maintaining strength is crucial.
Aerospace and Automotive: The lightweight and durable nature of graphene composites is advantageous in aerospace and automotive industries, where reducing weight while maintaining strength is crucial.