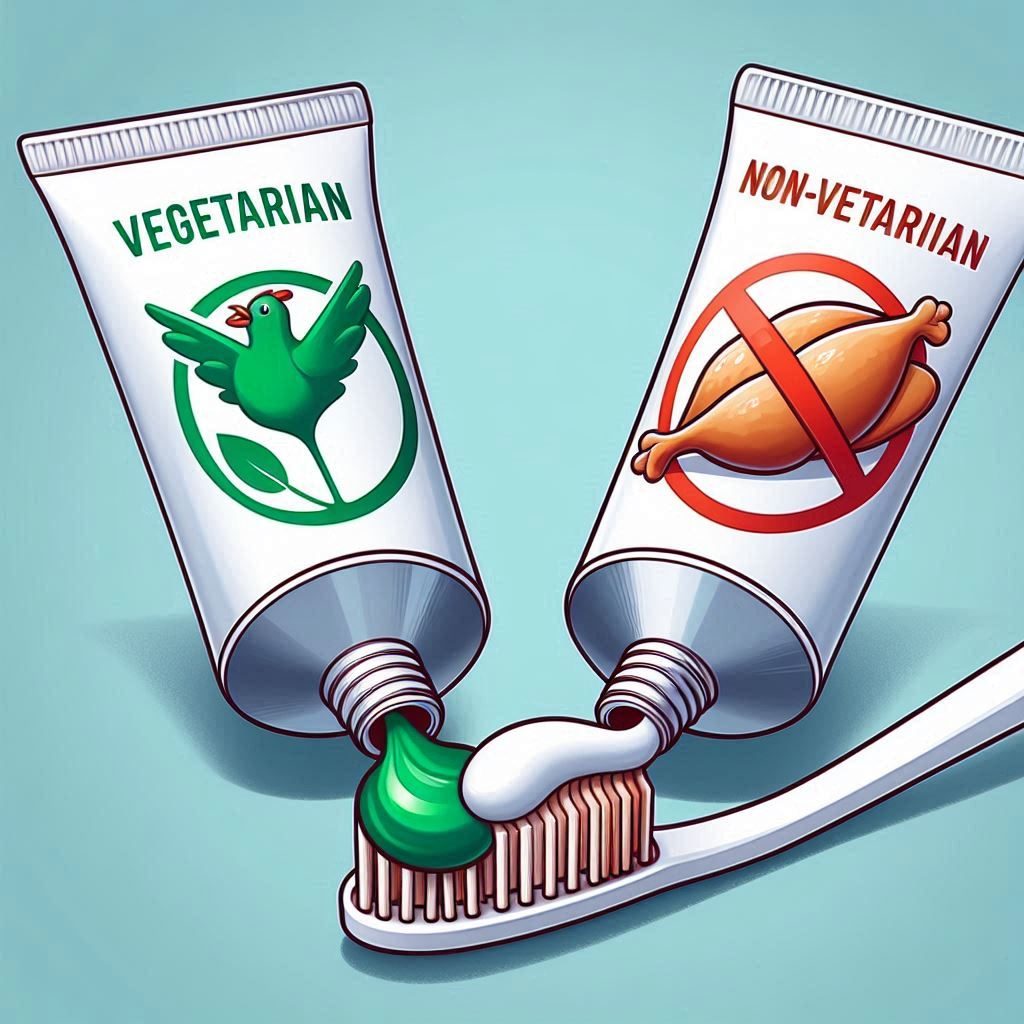
Vegetarian vs Non Vegetarian Toothpaste
The Great toothpaste debate
You might be surprised to know that the humble toothpaste you use everyday can be a subject of debate, especially for vegetarians and vegans. To determine whether your toothpaste is vegetarian or not, we need to look at its ingredients. Many common toothpaste ingredients are plant based and hence vegetarian friendly, these include:
- Water: The primary ingredient in most toothpastes.
- Humectants: Substances that prevent drying, like glycerin.
- Abrasives: To scrub away plaque, often derived from minerals like calcium carbonate or silica.
- Foaming agents: To create that bubbly lather, typically sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS).
- Flavoring agents: For that fresh taste, often synthetic or derived from plants.
- Thickeners: To give toothpaste its consistency, like xanthan gum.

The controversial ingredient : Glycerin
One ingredient that often raises questions is glycerin. While it can be derived from plant sources, it can also be derived from animal fats. This makes it a potential issue for strict vegetarians and vegans.
Vegetarian Toothpaste: A growing market
Due to increasing consumer awareness about animal derived products, many brands now offer vegetarian and vegan toothpaste options. These products explicitly mention on their packaging that they are free from animal derived ingredients.
Non Vegetarian Toothpaste: The Hidden Ingredients
Most conventional toothpastes don’t explicitly state whether they are vegetarian or non-vegetarian. This is where it can get tricky. If you’re following a strict vegetarian or vegan diet, it’s essential to read the ingredient list carefully. Look for terms like glycerin and consider contacting the manufacturer to inquire about its source.
Making an Informed Choice
If you’re concerned about using vegetarian or vegan toothpaste, here are some tips:
- Read labels carefully: Look for terms like “vegetarian” or “vegan” on the packaging.
- Check for glycerin: If glycerin is listed, contact the manufacturer to inquire about its source.
- Opt for certified vegetarian or vegan brands: Many brands offer certifications to assure consumers about their product’s ethical status.
- Consider natural alternatives: Some natural toothpaste brands use entirely plant-based ingredients.
What is HAP?
Hydroxyapatite (HAP) is a mineral compound naturally found in human teeth and bones. Its role in dental care is to remineralize tooth enamel, helping to strengthen and protect teeth from decay.
Synthetic HAP vs. Animal Origin HAP
There are two primary sources of HAP used in toothpaste:
- Synthetic HAP: This is a lab-created version of HAP. It’s produced through a chemical process that doesn’t involve any animal-derived materials. This makes it a suitable option for vegetarians and vegans.
- Animal Origin HAP: Traditionally, HAP was extracted from animal bones and tissues. While effective, this source raised concerns among consumers who prefer products without animal-derived ingredients.
Benefits of HAP in Toothpaste
Regardless of its source, HAP offers several benefits for oral health:
- Remineralization: It helps repair weakened tooth enamel.
- Sensitivity reduction: It can help alleviate tooth sensitivity.
- Whitening: Some formulations claim to have whitening properties.
- Anti-cavity protection: By strengthening enamel, it can help prevent cavities.
Choosing the Right Toothpaste
If you’re a vegetarian or vegan, opting for a toothpaste with synthetic HAP is the way to go. However, it’s essential to check the product label to ensure it explicitly states “synthetic HAP.”
For those not concerned about animal-derived ingredients, either synthetic or animal-origin HAP can be effective. Ultimately, the best toothpaste for you depends on your specific oral health needs and preferences.
Important Note: While HAP is generally considered safe for most people, individuals with specific allergies or sensitivities should consult with a dentist before using HAP-containing toothpaste.
Historically, hydroxyapatite (HAP) used in toothpaste was primarily sourced from animal bones and tissues. This process often involved:
- Procurement of animal byproducts: These byproducts, such as bones and cartilage, were obtained from slaughterhouses or other animal processing facilities.
- Cleaning and processing: The animal materials underwent a rigorous cleaning and processing process to remove impurities and prepare them for HAP extraction.
- Extraction of HAP: Through chemical processes, HAP was extracted from the animal matter.
While it’s difficult to pinpoint specific animals that faced the most cruelty, the general understanding is that animals raised for meat consumption were the primary source of these byproducts. This includes:
- Cattle: A significant source of bones and other tissues used in HAP production.
- Pigs: Another common source of animal byproducts.
- Poultry: While less commonly used for HAP, poultry byproducts might also have been involved.
It’s important to emphasize that the conditions under which these animals were raised and slaughtered are a complex issue with widespread implications for animal welfare. The focus on synthetic HAP in recent years is a direct response to the ethical concerns associated with animal-derived ingredients.
The use of animal-derived ingredients in products, including toothpaste, has raised significant ethical concerns. These concerns often revolve around:
- Animal welfare: The conditions in which animals are raised for food consumption often come under scrutiny. Practices such as intensive farming and slaughter methods can be seen as inhumane.
- Environmental impact: The meat industry contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution.
- Public health: There are concerns about the potential health risks associated with consuming animal products, including antibiotic resistance and zoonotic diseases.
Beyond Animal-Derived HAP: Mineral Alternatives
As consumer awareness about animal welfare and environmental issues grows, the demand for cruelty-free and sustainable products has increased. This has led to the development of alternative sources for minerals like calcium, which is a key component of teeth.
Some potential alternatives to animal-origin HAP include:
- Plant-based calcium: Derived from sources like algae, seaweed, or certain plant seeds.
- Synthetic calcium compounds: Created in laboratories without the use of animal products.
- Mineral-rich water: Containing calcium and other essential minerals.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of these alternatives in oral care may vary, and more research is needed to assess their long-term benefits.
Why Synthetic HAP Might Be a Better Choice
While both synthetic and animal-origin HAP can effectively remineralize teeth, there are several reasons why synthetic HAP is often considered a preferable option:
- Ethical Considerations:
- Animal welfare: The production of animal-origin HAP involves the use of animal byproducts, which raises ethical concerns for many consumers.
- Sustainability: The demand for animal-origin HAP can contribute to environmental issues and impact animal populations.
- Consistency and Purity:
- Controlled production: Synthetic HAP is produced in a controlled laboratory environment, ensuring consistent quality and purity.
- Reduced risk of contaminants: Animal-derived products can potentially contain contaminants or impurities.
- Allergy Concerns:
- Lower allergy risk: Some individuals may have allergies or sensitivities to animal-derived products. Synthetic HAP eliminates this risk.
- Consumer Preference:
- Growing demand: There’s a growing trend towards plant-based and cruelty-free products, making synthetic HAP a more appealing choice for many consumers.